Supported SoCs
Ameba SoC |
RTL8721Dx |
RTL8720E |
RTL8726E |
RTL8713E |
RTL8730E |
RTL8721F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Supported |
Y |
N |
N |
N |
Y |
Y |
USB Overview
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a standard serial communication interface designed to interconnect host controllers and peripheral devices. Its core features include:
Plug-and-Play: Enables hot-swappable capability without requiring system reboots for device connection/disconnection.
Standardized Specifications: Defines unified electrical interfaces and layered communication protocols to ensure cross-vendor interoperability.
Multi-Functionality Support: Accommodates multiple device classes through its tiered architecture, including communication, human interface, mass storage, and audio/video devices.
Integrated Power Delivery: Incorporates VBUS power rails (5V nominal), eliminating external power supplies for bus-powered devices.
USB IF (USB Implementers Forum) oversees the development of USB technical standards, maintains compliance testing tools, administers certification programs and related technologies.
The complete USB specification suite, including electrical, mechanical, and protocol layer documentation, is accessible at http://www.usb.org/developers.
Hardware Features
Supports device mode
Supports USB 2.0 full-speed (12 Mbps) mode
Supports DMA/slave mode
Endpoint configurations:
EP0: INOUT (for Control transfer only)
EP1: IN
EP2: OUT
EP3: IN
EP4: OUT
EP5: INOUT
Note
One and only one periodic IN endpoint is supported.
Shared FIFO with following configurations:
Total FIFO depth: 768 DWORD
Shared receive FIFO: 472 DWORD (max)
Shared non-periodic transmit FIFO: 32 DWORD (max)
Dedicated periodic transmit FIFO: 256 DWORD (max)
Note
8 DWORD FIFO shall be reserved for DMA registers in DMA mode.
Supports host, device and OTG modes
Supports USB 2.0 high-speed (480 Mbps) and full-speed (12 Mbps) modes
Supports DMA/slave mode
Endpoint configurations in device mode:
EP0: INOUT (for Control transfer only)
EP1: IN
EP2: OUT
EP3: IN
EP4: OUT
EP5: INOUT
Note
One and only one periodic IN endpoint is supported.
Supports 8 channels/pipes in host mode
Shared FIFO with following configurations:
Total FIFO depth: 1024 DWORD
Host mode:
Shared receive FIFO: 512 DWORD (max)
Shared non-periodic transmit FIFO: 256 DWORD (max)
Shared periodic transmit FIFO: 256 DWORD (max)
Device mode:
Shared RX FIFO: 512 DWORD (max)
Shared non-periodic transmit FIFO: 256 DWORD (max)
Dedicated periodic transmit FIFO: 256 DWORD (max)
Note
8 DWORD FIFO shall be reserved for DMA registers in DMA mode.
Integrated UTMI+ PHY
External hub connection support in host mode
Automatic ping in host mode
Supports host and device modes
Supports USB 2.0 high-speed (480 Mbps) and full-speed (12 Mbps) modes
Supports DMA/slave mode
Endpoint configurations in device mode:
EP0: INOUT (for Control transfer only)
EP1: IN
EP2: INOUT
EP3: INOUT
EP4: IN
EP5: OUT
EP6: INOUT
EP7: OUT
Supports 12 channels/pipes in host mode
Shared FIFO with following configurations:
Total FIFO depth: 1024 DWORD
Host mode:
Shared receive FIFO: 1024 DWORD (max)
Shared non-periodic transmit FIFO: 1024 DWORD (max)
Shared periodic transmit FIFO: 1024 DWORD (max)
Device mode:
Shared RX FIFO: 1024 DWORD (max)
6 dedicated transmit FIFOs for device IN transfers, max depth of each Tx FIFO:
Tx FIFO 0: 32
Tx FIFO 1: 16
Tx FIFO 2: 256
Tx FIFO 3: 32
Tx FIFO 4: 256
Tx FIFO 5: 128
Note
12 DWORD FIFO shall be reserved for DMA registers in DMA mode.
Integrated UTMI+ PHY
External hub connection support in host mode
Automatic ping in host mode
Software Stack Overview
Software Features
Supports USB2.0 full-speed device mode
Supports DMA and slave modes
Modular layered architecture with asynchronous callback-based API communication between protocol layers, optimized to minimize MCU real-time scheduling overhead
Supports standard USB IF device classes: CDC ACM, HID, UAC, etc.
Supports USB solution examples: transparent communication, HID, audio, etc.
Full descriptor customization:
VID and PID
String descriptors
Endpoint mapping
Configurable device core driver parameters
Speed mode
Data FIFO depth (only for dedicated FIFO mode)
Core ISR priority
Extended interrupt masks
Supports host and device modes
Supports USB2.0 high-speed and full-speed modes
Supports DMA and slave modes
Modular layered architecture with asynchronous callback-based API communication between protocol layers, optimized to minimize MCU real-time scheduling overhead
Supports following standard USB IF classes:
Host: CDC ACM, CDC ECM, MSC, UVC, etc.
Device: CDC ACM, HID, MSC, UAC, etc.
Supports following USB solution examples:
Host: transparent communication, ethernet communication, mass storage, video, etc
Device: transparent communication, HID, mass storage, audio, etc.
DRD: host mass storage and device mass storage
Full descriptor customization:
VID and PID
String descriptors
Endpoint mapping
Configurable host/device core driver parameters
Speed mode
Data FIFO depth (only for dedicated FIFO mode)
Core ISR/thread priority
Extended interrupt masks
Supports host and device modes
Supports USB2.0 high-speed and full-speed modes
Supports DMA and slave modes
Modular layered architecture with asynchronous callback-based API communication between protocol layers, optimized to minimize MCU real-time scheduling overhead
Supports following standard USB IF classes:
Host: CDC ACM, CDC ECM, MSC, UVC, etc.
Device: CDC ACM, HID, MSC, UAC, etc.
Supports following USB solution examples:
Host: transparent communication, ethernet communication, mass storage, video, etc
Device: transparent communication, HID, mass storage, audio, etc.
DRD: host mass storage and device mass storage
Full descriptor customization:
VID and PID
String descriptors
Endpoint mapping
Configurable host/device core driver parameters
Speed mode
Data FIFO depth (only for dedicated FIFO mode)
Core ISR/thread priority
Extended interrupt masks
Software Architecture
The architecture of USB software stack:
Where:
USB HAL driver: Implements SoC-specific hardware driver for power management and phy calibration, exposing unified HAL API to upper-layer core drivers.
USB host/device core drivers: Integrates USB IP-specific hardware driver, host/device controller driver, enumeration state machine and transfer scheduling algorithms, exposing unified core API for designers to develop classes and applications.
USB host/device class drivers: Delivers USB-IF class-compliant drivers via class-specific API, enabling rapid deployment of standard USB solutions
USB host/device applications: Provides reference designs for USB solutions
File Organization
USB HAL Driver
Path |
Description |
|---|---|
|
USB HAL API definition header file |
USB Core Driver
Path |
Description |
|
USB common core driver API definition header file |
|
USB device core driver API definition header file |
|
USB device core driver static library file |
Path |
Description |
|
USB common core driver API definition header file |
|
USB device core driver API definition header file |
|
USB host core driver API definition header file |
|
USB DRD core driver static library file for DRD solution |
|
USB device core driver static library file for device solution |
|
USB host core driver static library file for host solution |
Path |
Description |
|
USB common core driver API definition header file |
|
USB device core driver API definition header file |
|
USB host core driver API definition header file |
|
USB DRD core driver static library file for DRD solution |
|
USB device core driver static library file for device solution |
|
USB host core driver static library file for host solution |
USB Class Driver
Path |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CDC ACM device class driver |
|
Composite device class driver |
|
HID device class driver |
|
INIC device class driver (non-standard) |
|
MSC device class driver |
|
UAC device class driver |
|
Vendor-specific device class driver |
|
CDC ACM host class driver |
|
CDC ECM host class driver |
|
MSC host class driver |
|
UVC host class driver |
|
Vendor-specific host class driver |
USB Application
Path |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Transparent communication device example based on CDC ACM device class |
|
Composite device example based on CDC ACM and HID device classes |
|
Composite device example based on CDC ACM and UAC device classes |
|
Composite device example based on HID and UAC device classes |
|
HID device example |
|
INIC device example |
|
Mass storage device example based on MSC device classes |
|
Audio device example based on UAC device classes |
|
Vendor-specific device example |
|
Transparent communication host example based on CDC ACM host class |
|
Ethernet communication host example based on CDC ECM host class |
|
Mass storage host example based on MSC host classe |
|
Video host example based on UVC host classe |
|
Vendor-specific host example |
|
Ethernet communication bridge example based on CDC ECM host class |
|
DRD example based on MSC host class and MSC device classe |
HAL Driver
Overview
USB HAL driver implements SoC-specific USB power management, interrupt handling and phy calibration interfaces, defines system-level preprocessor constants, exposes unified HAL API to upper-layer drivers.
USB HAL API
USB HAL driver is defined with usb_hal_driver_t type:
typedef struct {
int(* init)(u8 mode);
int(* deinit)(void);
void(* enable_interrupt)(u8 priority);
void(* disable_interrupt)(void);
void(* register_irq_handler)(void *handler, u8 priority);
void(* unregister_irq_handler)(void);
usb_cal_data_t *(* get_cal_data)(u8 mode);
void (*cg)(u32 ms);
} usb_hal_driver_t;
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
SoC-specific USB initialization |
deinit |
SoC-specific USB deinitialization |
enable_interrupt |
Enable USB interrupt |
disable_interrupt |
Disable USB interrupt |
register_irq_handler |
Register USB interrupt handler |
unregister_irq_handler |
Unregister USB interrupt handler |
get_cal_data |
Get SoC-specific USB PHY calibration data |
cg |
Clock gate process for USB power test |
And USB HAL driver defines following preprocessor constants used in upper-layer drivers:
Definition |
Description |
|---|---|
USB_REG_BASE |
Base address of USB registers |
USB_ADDON_REG_BASE |
Base address of USB AddOn registers |
USB_MAX_ENDPOINTS |
Max number of endpoints supported in USB device mode |
USB_MAX_PIPES |
Max number of pipes supported in USB host mode |
USB_VID |
Realtek USB VID |
USB_PID |
Realtek USB PID |
Note
USB HAL driver is built into USB host/device/DRD core library as default and customization is not allowed.
USB PHY calibration data is determined by Realtek during manufacturing and developer-side re-calibration is not allowed, for suspected calibration-related compatibility issues (e.g., USB enumeration failures, intermittent disconnection/reconnection issues), contact Realtek FAE for help.
Host Core Driver
Host Core Driver API Overview
USB host core driver API definition header file: {SDK}/component/usb/host/core/usbh.h
API for Host Class Drivers
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbh_register_class |
Register a class driver, the class driver is defined by type usbh_class_driver_t. Refer to Class callback for details. |
usbh_unregister_class |
Un-register a class driver. |
usbh_alloc_pipe |
Allocate a pipe for the specified endpoint address. |
usbh_free_pipe |
Free a pipe. |
usbh_open_pipe |
Open a pipe as per specified pipe number and endpoint info. |
usbh_close_pipe |
Close a pipe. |
usbh_reactivate_pipe |
Reactivate the request in a specific pipe. |
usbh_get_configuration |
Get the configuration index against specific subclass. |
usbh_set_configuration |
Set the configuration index for bNumConfigurations>1 in device descriptor. |
usbh_get_interface |
Get the interface index as per the specific class, subclass and protocol. |
usbh_set_interface |
Set activate interface index. |
usbh_get_interface_descriptor |
Get the interface descriptor as per specific interface index and alternate setting. |
usbh_get_raw_configuration_descriptor |
Get the raw configuration descriptor data. |
usbh_get_device_descriptor |
Get device descriptor. |
usbh_get_interval |
Get the actual interval value as per endpoint type and bInterval. |
usbh_set_toggle |
Set PID toggle for specific pipe. |
usbh_get_toggle |
Get the current PID toggle of specific pipe. |
usbh_get_ep_type |
Get the endpoint type of specific pipe. |
usbh_get_urb_state |
Get the current URB state of specific pipe. |
usbh_notify_class_state_change |
Notify host core that class state has been changed. |
usbh_notify_urb_state_change |
Notify host core that URB state has been changed. |
usbh_ctrl_set_interface |
Send SET_INTERFACE standard request to device. |
usbh_ctrl_set_feature |
Send SET_FEATURE standard request to device. |
usbh_ctrl_clear_feature |
Send CLEAR_FEATURE standard request to device. |
usbh_ctrl_request |
Send control request to device. |
usbh_bulk_receive_data |
Receive BULK IN data from device. |
usbh_bulk_send_data |
Send BULK OUT data to device. |
usbh_intr_receive_data |
Receive INTR IN data from device. |
usbh_intr_send_data |
Send INTR OUT data to device. |
usbh_isoc_receive_data |
Receive ISOC IN data from device. |
usbh_isoc_send_data |
Send ISOC OUT data to device. |
usbh_get_current_frame |
Get the current frame number. |
usbh_get_last_transfer_size |
Get the last transfer data size of specific pipe. |
usbh_enter_suspend |
Enter/Exit suspend state. |
usbh_port_test_ctrl |
Send port test request, only for CTS test. |
Class Callback
USB host class driver is defined by type usbh_class_driver_t as a group of callbacks:
typedef struct {
u8 class_code;
u8(*attach)(struct _usb_host_t *host);
u8(*detach)(struct _usb_host_t *host);
u8(*setup)(struct _usb_host_t *host);
u8(*process)(struct _usb_host_t *host);
u8(*sof)(struct _usb_host_t *host);
u8(*nak)(struct _usb_host_t *host, u8 pipe_num);
} usbh_class_driver_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
class_code |
Class code specified by USB IF. |
attach |
Called when SET_CONFIGURATION request is successfully responsed. |
detach |
Called when device is disconnected. |
setup |
Called after class attached to process class-specific control requests. |
process |
Cyclically called after class setup to process class-specific transfers. |
sof |
Called at SOF interrupt for class-specific timing process. |
nak |
Called at NAK interrupt of specific pipe. |
API for Host Applications
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbh_init |
Initialize USB host core driver with configuration parameters defined by type Refer to USB Host Core Driver Configuration. |
usbh_deinit |
De-initialize USB host core driver. |
usbh_get_status |
Get device connection status: 0 - Disconnected, 1 - Connected. |
usbh_reenumerate |
Redo enumeration. |
USB Host Core Driver Configuration
USB host core driver provides type usbh_config_t to define the core driver configuration parameters:
typedef struct {
u32 ext_intr_en;
u16 rx_fifo_depth;
u16 nptx_fifo_depth;
u16 ptx_fifo_depth;
u8 main_task_priority;
u8 isr_task_priority;
u8 alt_max;
u8 speed : 2;
u8 dma_enable : 1;
u8 sof_tick_en : 1;
} usbd_config_t;
Where:
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
ext_intr_en |
Enable optional extended USB interrupts. Set it to 0 to disable all optional interrupts and set it to following values to enable specific interrupt(s) as needed by applications:
|
rx_fifo_depth |
Share receive FIFO depth, only for SoCs with dedicated USB FIFO. Min value 16 and max value restricted by SoC hardware, refer to Hardware Features. |
nptx_fifo_depth |
Share non-periodic transmit FIFO depth, only for SoCs with dedicated USB FIFO. Min value 16 and max value restricted by SoC hardware, refer to Hardware Features. |
ptx_fifo_depth |
Share periodic transmit FIFO depth, only for SoCs with dedicated USB FIFO. Min value 16 and max value restricted by SoC hardware, refer to Hardware Features. |
main_task_priority |
The priority of main task in USB host core driver, the main task processes the USB host messages. |
isr_task_priority |
The priority of ISR task in USB host core driver, the ISR task processes the USB host interrupts. |
alt_max |
The max number of alternate settings allowed in interface descriptor. |
speed |
USB host speed mode, valid values:
|
dma_enable |
Enable DMA mode. |
sof_tick_en |
Flag to set the timing strategy of USB host core driver. The timing strategy is used to trigger periodic transfers based on the bInterval value of device endpoint descriptor and to detect transfer timeouts:
|
Note
The configured total FIFO depth rx_fifo_depth + nptx_fifo_depth + ptx_fifo_depth shall not exceed the max total FIFO depth supported by the SoC hardware, refer to Hardware Features.
Device Core Driver
Device Core Driver API Overview
USB device core driver API definition header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/core/usbd.h
API for Device Class Drivers
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_register_class |
Register a device class driver, called in class initialization function. The class driver is defined by type usbd_class_driver_t, refer to Class Callback. |
usbd_unregister_class |
Un-register a class, called in class de-initialization function. |
usbd_ep_init |
Initialize an endpoint, typically called in following scenarios:
|
usbd_ep_deinit |
Deinitialize an endpoint, typically called in following scenarios:
|
usbd_ep_transmit |
Initiates an IN transfer to the USB host through a specified endpoint. The transfer executes asynchronously: function return doesn’t indicate completion. Check transfer status via ep_data_in/ep0_data_in callback of the device class driver. ZLP will be automatically transmitted as needed by device core driver. |
usbd_ep_receive |
Prepares to receive OUT transfer data from the USB host through a specified endpoint. The transfer executes asynchronously: function return doesn’t indicate completion. Retrieved data is available via the ep_data_out/ep0_data_out callback of the device class driver. |
usbd_ep_set_stall |
Sets the specified endpoint to STALL state. |
usbd_ep_clear_stall |
Clears the STALL state of the specified endpoint. |
usbd_ep_is_stall |
Checks whether the specified endpoint is in STALL state. |
usbd_get_str_desc |
Converts ASCII strings to UNICODE16-encoded USB string descriptors. Note: The destination buffer must accommodate twice the source length plus 2 bytes (for the length and type fields of string descriptor). |
Class Callback
USB device class driver is defined by type usbd_class_driver_t as a group of callbacks:
typedef struct _usbd_class_driver_t {
u16(*get_descriptor)(usb_dev_t *dev, usb_setup_req_t *req, u8 *buf);
u8(*set_config)(usb_dev_t *dev, u8 config);
u8(*clear_config)(usb_dev_t *dev, u8 config);
u8(*setup)(usb_dev_t *dev, usb_setup_req_t *req);
u8(*sof)(usb_dev_t *dev);
u8(*suspend)(usb_dev_t *dev);
u8(*resume)(usb_dev_t *dev);
u8(*ep0_data_in)(usb_dev_t *dev, u8 status);
u8(*ep0_data_out)(usb_dev_t *dev);
u8(*ep_data_in)(usb_dev_t *dev, u8 ep_addr, u8 status);
u8(*ep_data_out)(usb_dev_t *dev, u8 ep_addr, u16 len);
void (*status_changed)(usb_dev_t *dev, u8 old_status, u8 status);
} usbd_class_driver_t;
Where:
API |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
get_descriptor |
Yes |
Called during enumeration when host requests USB descriptors. The class driver must return the descriptor data buffer and length againt the wValue value of host setup request:
Refer to Device Descriptor Customization for USB descriptors. |
set_config |
Yes |
Called upon SET_CONFIGURATION request in ADDRESSED state. The device class driver must:
|
clear_config |
Yes |
Called when:
Typically, the device class driver shall call usbd_ep_deinit to deinitialize the endpoints. |
setup |
Yes |
Called at control transfer setup phase to handle class-specific control requests:
|
ep_data_in |
No |
Called when bulk/interrupt/isochronous IN transfer done for IN transfer status indication. The device class driver may mark endpoint ready for next transfer or retry failed transfers. |
ep_data_out |
No |
Called when bulk/interrupt/isochronous OUT transfer done for received data handling. Typically, the device class driver shall:
|
ep0_data_in |
No |
Called when control IN transfer done for IN transfer status indication. |
ep0_data_out |
No |
Called when control OUT transfer done for received data handling. Note: the device driver does not need to re-enable the control OUT transfer since it is automatically done in core driver. |
sof |
No |
Called upon SOF interrupt (GINTSTS.Sof) for timing-sensitive operations (e.g., UAC clock synchronization). |
suspend |
No |
Called upon suspend interrupt (GINTSTS.USBSusp) for power management. |
resume |
No |
Called upon resume interrupt (GINTSTS.WkUpInt) for resource recovery. |
status_changed |
Yes |
Called upon connection state changed for hot-plug support (e.g., do reinitialization on host disconnection), refer to Device Connection Status Detection. |
Note
All the above device class driver callback functions are invoked in interrupt context. Time-consuming or blocking operations must not be executed within these callback functions.
API for Device Applications
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_init |
Initialize USB device core driver with configuration defined by type |
usbd_deinit |
Deinitialize USB device core driver |
usbd_get_status |
Get USB attach status with return value defined by
|
usbd_get_bus_status |
Get USB bus status. Return HAL_OK on success, with the status parameter containing USB bus status information represented
as a bitwise combination of
|
usbd_wake_host |
Sends a remote wakeup signal to the USB host to resume communication |
USB Device Core Driver Configuration
USB device core driver provides type usbd_config_t to define the core driver configuration parameters:
typedef struct {
u32 nptx_max_epmis_cnt;
u32 ext_intr_en;
u16 rx_fifo_depth;
u16 ptx_fifo_depth[USB_MAX_ENDPOINTS - 1];
u8 speed;
u8 isr_priority;
u8 isr_in_critical : 1;
u8 dma_enable : 1;
u8 intr_use_ptx_fifo : 1;
} usbd_config_t;
Where:
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
nptx_max_epmis_cnt |
Threshold count of EPMis interrupts for non-periodic IN transfers, only for SoCs with shared USB FIFO |
ext_intr_en |
Optional USB interrupt enable flags:
|
rx_fifo_depth |
Receive FIFO depth in DWORD (must not exceed hardware limits), only for SoC with dedicated FIFO, refer to Hardware Features. |
ptx_fifo_depth |
Transmit FIFO depth in DWORD (must not exceed hardware limits), ptx_fifo_depth[n] corresponds to transmit FIFO n+1 (transmit FIFO index 0 uses hardware defaults). Only for SoC with dedicated FIFO, refer to Hardware Features. |
speed |
USB device speed mode:
|
isr_priority |
Priority level of USB interrupt service routine |
isr_in_critical |
Execute USB ISR in critical region (0: disabled, 1: enabled) |
dma_enable |
DMA mode control (0: disabled, 1: enabled) |
intr_use_ptx_fifo |
Use dedicated periodic transmit FIFO for interrupt IN transfers (0: disabled, 1: enabled), only for SoCs with shared USB FIFO |
Note
For SoCs with shared USB FIFO, no FIFO depth configuration is required.
For SoCs with dedicated USB FIFO, observe the following constraint:
rx_fifo_depth + Σ(ptx_fifo_depth[n]) <= Hardware total FIFO depth
Refer to Hardware Features.
Host Solutions
Transparent Communication Host Solution
Overview
The CDC ACM (Abstract Control Model) class, a subclass of the Communication Device Class (CDC), enables transparent communication applications.
SDK provides:
Standard CDC ACM host class driver with pipe configurations:
2 control IN/OUT pipes
1 interrupt IN pipe
1 bulk IN pipe
1 bulk OUT pipe
Transparent communication application example with features:
Compatible with CDC ACM devices defined by Transparent Communication Device Solution
Supports data integrity verification, lifetime testing and performance benchmarking
Supports hot-plug operation
Class Driver
Source Location
{SDK}/component/usb/host/cdc_acm
API for Applications
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/host/cdc_acm/usbh_cdc_acm.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbh_cdc_acm_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handler, refer to Application Callback. |
usbh_cdc_acm_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
usbh_cdc_acm_set_line_coding |
Sends SET_LINE_CODING control request |
usbh_cdc_acm_get_line_coding |
Sends GET_LINE_CODING control request |
usbh_cdc_acm_set_control_line_state |
Sends SET_CONTROL_LINE_STATE control request |
usbh_cdc_acm_transmit |
Initiates bulk OUT transfer |
usbh_cdc_acm_receive |
Initiates bulk IN transfer |
usbh_cdc_acm_notify_receive |
Initiates interrupt IN transfer to get device status notifications |
usbh_cdc_acm_get_bulk_ep_mps |
Retrieves max packet size of the device bulk IN endpoint |
Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbh_cdc_acm_cb_t:
typedef struct {
int(* init)(void);
int(* deinit)(void);
int(* attach)(void);
int(* detach)(void);
int(* setup)(void);
int(* notify)(u8 *buf, u32 len);
int(* receive)(u8 *buf, u32 len);
int(* transmit)(usbh_urb_state_t state);
int(* line_coding_changed)(usbh_cdc_acm_line_coding_t *line_coding);
} usbh_cdc_acm_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called when class driver initialized, used to allocate application-specific resources |
deinit |
Called when class driver de-initialized, used to release application-specific resources |
attach |
Called when device attached, used to report device connection status |
detach |
Called when device detached, used to report device disconnection status |
setup |
Called when device setup done, used to indicate that device is ready for bulk transfer |
notify |
Called when interrupt IN transfer completed, used to report interrupt notifications |
receive |
Called when bulk IN transfer completed, used for application to handle the received bulk IN data |
transmit |
Called when bulk OUT transfer completed, used to report bulk OUT transfer completion status |
line_coding_changed |
Called when device line coding parameters change |
Application Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbh_cdc_acm
The example defines an USB CDC ACM host, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for USB transparent communication host applcations.
Ethernet Communication Host Solution
Overview
The CDC ECM (Ethernet Control Model) class, a subclass of the Communication Device Class (CDC), enables network device connectivity via USB.
SDK provides:
Standard CDC ECM host class driver with pipe configurations:
2 control IN/OUT pipes
1 interrupt IN pipe
1 bulk IN pipe
1 bulk OUT pipe
CDC ECM host application example with following features:
CDC ECM device enumeration and basic communication testing
Validates CDC ECM protocol compliance
CDC ECM bridge application example with following features:
Network packet routing between ECM devices and routers
Implements Ethernet frame translation
Class Driver
Location
{SDK}/component/usb/host/cdc_ecm
API for Applications
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/host/cdc_ecm/usbh_cdc_ecm_hal.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbh_cdc_ecm_do_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handler, refer to Application Callback. |
usbh_cdc_ecm_do_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
usbh_cdc_ecm_process_mac_str |
Retrieves the MAC address information of attached CDC ECM device |
usbh_cdc_ecm_send_data |
Initiates bulk OUT data transfer |
usbh_cdc_ecm_get_connect_status |
Queries device connection status |
usbh_cdc_ecm_get_receive_mps |
Retrieves max packet size of the device bulk IN endpoint |
Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usb_report_data:
typedef void (*usb_report_data)(u8 *buf, u32 len);
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usb_report_data |
Processes received bulk IN network packets |
Application Example
SDK provides two CDC ECM host application examples.
CDC ECM Host Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbh_cdc_ecm
The example defines an USB CDC ECM host, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for CDC ECM host applcations.
CDC ECM Bridge Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbh_wifi_bridge
The example defines an USB CDC ECM bridge, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for CDC ECM bridge applcations.
Mass Storage Host Solution
Overview
The MSC (Mass Storage Class) host provides support for mass storage devices using the SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) command set for data access operations.
SDK provides:
Standard MSC host class driver with following features:
Supports BOT (Bulk-Only Transport) protocol
Pipe configurations:
2 control IN/OUT pipes
1 bulk IN pipe
1 bulk OUT pipe
Reference MSC host application example with these features:
Supports FAT32-formatted MSC devices
Supports basic data access testing with FATFS API
Class Driver
Location
{SDK}/component/usb/host/msc
API for Applications
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/host/msc/usbh_msc.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbh_msc_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handler, refer to Application Callback. |
usbh_msc_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbh_msc_cb_t:
typedef struct {
int(* attach)(void);
int(* detach)(void);
int(* setup)(void);
} usbh_msc_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
attach |
Called when device attached, used to report device connection status |
detach |
Called when device detached, used to report device disconnection status |
setup |
Called when device setup done, used to indicate that device is ready for bulk transfer |
FATFS Disk Driver API
The class driver defines a FATFS disk driver USB_disk_Driver typed with ll_diskio_drv:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
disk_initialize |
Initializes USB disk |
disk_deinitialize |
Deinitializes USB disk |
disk_status |
Returns disk status (RES_OK/RES_ERROR) |
disk_read |
Reads data from USB disk (sector-aligned) |
disk_write |
Writes data to USB disk (requires _USE_WRITE set in FATFS) |
disk_ioctl |
Implements FATFS IO control commands:
|
Application Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbh_msc
The example defines an USB MSC host, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for USB mass storage host applcations.
Video Host Solution
Overview
The UVC (USB Video Class) host enables detection, configuration, and management of UVC-compliant devices (e.g., webcams, video capture cards) for image/video streaming applications including:
Surveillance systems
Industrial inspection
Medical imaging
Live video streaming
SDK provides:
Standard UVC host class driver with following features:
Supports UVC 1.5 High-Speed/Full-Speed devices
Supports video formats: MJPEG/YUV420/H.264
Configurable resolution and frame rate
Maximum throughput: 6 Mbps
Pipe configuration:
2 control IN/OUT pipes
1 isochronous IN Pipe
UVC host application example with following configurations:
CONFIG_USBH_UVC_APP_SIMPLE: Capture frames for performance benchmarking
CONFIG_USBH_UVC_APP_VFS: Stores MJPEG/H.264 frames to SD card via VFS
CONFIG_USBH_UVC_APP_HTTPC: Streams frames to HTTP server
Class Driver
Location
{SDK}/component/usb/host/uvc
API for Applications
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/host/uvc/usbh_uvc_intf.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbh_uvc_init |
Initializes class driver with application callbacks, refer to Application Callback. |
usbh_uvc_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
usbh_uvc_stream_on |
Activates video streaming |
usbh_uvc_stream_off |
Terminates video streaming |
usbh_uvc_stream_state |
Returns streaming status (STREAMING_OFF/STREAMING_ON) |
usbh_uvc_set_param |
Configures video parameters (resolution, frame rate, format) |
usbh_uvc_get_frame |
Captures a video frame from frame buffer |
usbh_uvc_put_frame |
Releases captured frame buffer for reuse |
Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbh_uvc_cb_t:
typedef struct {
int(* init)(void);
int(* deinit)(void);
int(* attach)(void);
int(* detach)(void);
} usbh_uvc_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called when class driver initialized, used to allocate application-specific resources |
deinit |
Called when class driver de-initialized, used to release application-specific resources |
attach |
Called when device attached, used to report device connection status |
detach |
Called when device detached, used to report device disconnection status |
Application Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbh_uvc
The example defines an USB UVC host, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for USB video host applcations.
Vendor-Specific Host Solution
Overview
The vendor-specific class and corresponding example provide reference design for USB vendor-specific host applications.
SDK provides:
Vendor-specific host class driver with pipe configurations:
A pair of control IN/OUT pipes
A pair of bulk IN/OUT pipe
A pair of interrupt IN/OUT pipe
A pair of isochronous IN/OUT pipe
Vendor-specific host application example with following features:
Co-work with vendor-specific devices defined by Vendor-Specific Device Solution
Supports data integrity verification
Supports hot-plug
Class Driver
Source Location
{SDK}/component/usb/host/vendor
API for Applications
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/host/vendor/usbh_vendor.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbh_vendor_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handler, refer to Application Callback. |
usbh_vendor_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
usbh_vendor_bulk_transmit |
Initiates bulk OUT transfer |
usbh_vendor_bulk_receive |
Initiates bulk IN transfer |
usbh_vendor_intr_transmit |
Initiates interrupt OUT transfer |
usbh_vendor_intr_receive |
Initiates interrupt IN transfer |
usbh_vendor_isoc_transmit |
Initiates isochronous OUT transfer |
usbh_vendor_isoc_receive |
Initiates isochronous IN transfer |
usbh_vendor_get_bulk_ep_mps |
Retrieves max packet size of the device bulk IN endpoint |
usbh_vendor_get_intr_ep_mps |
Retrieves max packet size of the device interrupt IN endpoint |
Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbh_vendor_cb_t:
typedef struct {
int(* attach)(void);
int(* detach)(void);
int(* setup)(void);
int(* receive)(u8 ep_type, u8 *buf, u32 len);
int(* transmit)(u8 ep_type);
} usbh_vendor_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
attach |
Called when device attached, used to report device connection status |
detach |
Called when device detached, used to report device disconnection status |
setup |
Called when device setup done, used to indicate that device is ready for data transfer |
receive |
Called when IN transfer completed, used for application to handle the received IN data |
transmit |
Called when OUT transfer completed, used to report OUT transfer completion status |
Application Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbh_vendor
The example defines an USB vendor-specific host, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for USB vendor-specific host applcations.
Device Solutions
Audio Device Solution
Overview
The UAC (USB Audio Class) defines specifications for USB audio devices such as headsets, microphones and sound cards.
The audio parameters supported across UAC versions:
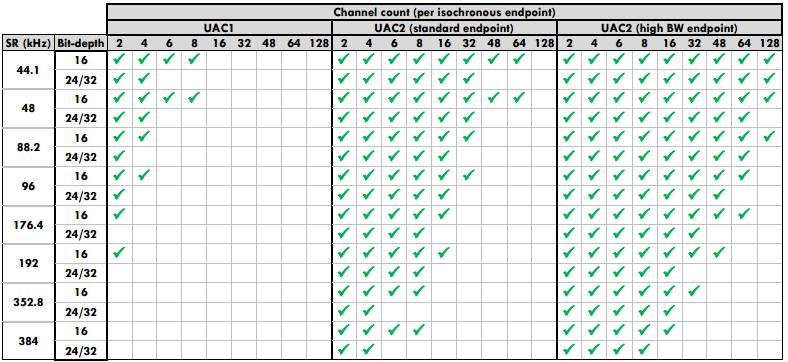
SDK provides:
UAC 1.0 (Full-Speed) class driver, speaker-only, supports following configurable audio parameters:
Sample Rate (kHz) |
Bit-depth |
Channel Count |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
||
44.1 |
16 |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
24/32 |
Y |
Y |
|||
48 |
16 |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
24/32 |
Y |
Y |
|||
96 |
16 |
Y |
Y |
||
24/32 |
Y |
||||
192 |
16 |
Y |
|||
24/32 |
|||||
UAC 2.0 (High/Full-Speed) class driver, speaker-only, supports following configurable audio parameters:
Sample Rate |
Bit-depth |
Channel Count |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
||
44.1 |
16 |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
24/32 |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
48 |
16 |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
24/32 |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
96 |
16 |
Y |
Y |
||
24/32 |
Y |
Y |
|||
192 |
16 |
Y |
|||
24/32 |
Y |
||||
Endpoint configuration:
1 control IN/OUT endpoint for host requests
1 isochronous OUT endpoint for audio data
Supports volume/mute control
Fully customizable descriptors
Supports hot-plug
Note
USB core driver doesn’t support UAC 2.0 high-bandwidth endpoints, max one isochronous OUT transfer per microframe is allowed.
The supported audio formats depend on the whole path of UAC host/device and hardware/software frameworks
Class Driver
Location
{SDK}/component/usb/device/uac
API for Applications
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/uac/usbd_uac.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_uac_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handler, refer to Application Callback |
usbd_uac_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
usbd_uac_config |
Configures audio parameters |
usbd_uac_start_play |
Starts receiving audio data to ring buffer |
usbd_uac_stop_play |
Stops audio data reception |
usbd_uac_read |
Reads audio data from ring buffer for playing |
usbd_uac_get_read_frame_cnt |
Gets queued audio frames count |
Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbd_uac_cb_t:
typedef struct {
usbd_audio_cfg_t in;
usbd_audio_cfg_t out;
void *audio_ctx;
int(* init)(void);
int(* deinit)(void);
int(* setup)(usb_setup_req_t *req, u8 *buf);
int(* set_config)(void);
void(* status_changed)(u8 old_status, u8 status);
void(* mute_changed)(u8 mute);
void(* volume_changed)(u8 volume);
void(* format_changed)(u32 freq, u8 ch_cnt);
void(* sof)(void);
} usbd_uac_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called during class driver initialization for application resource setup |
deinit |
Called during class driver deinitialization for resource cleanup |
setup |
Called during control transfer SETUP/DATA phases to handle application-specific control requests |
set_config |
Notifies application layer when UAC driver becomes operational |
status_changed |
Called upon USB attach status changes for application to support hot-plug events |
mute_changed |
Handles mute setting updates from USB host |
volume_changed |
Adjusts playback volume according to host-side volume changes |
format_changed |
Updates audio parameters (sample rate/channels) when modified by host |
sof |
Called upon SOF interrupt for clock synchronization |
Application Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbd_uac
The example defines an USB UAC speaker, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for USB audio device applcations.
Transparent Communication Device Solution
Overview
The CDC ACM (Abstract Control Model) class, a subclass of Communication Device Class (CDC), emulates COM ports for serial data transparent communication applications.
SDK provides:
Standard CDC ACM device class driver with following features:
Configurable bulk IN/OUT transfer lengths
Optional interrupt IN endpoint flexible for compatibility and bandwidth optimization
Endpoint configuration:
1 control IN/OUT endpoint to handle host control requests
1 interrupt IN endpoint for status reporting
1 bulk IN endpoint for data transmission
1 bulk OUT endpoint for data reception
CDC ACM device application example with following features:
Supports virtual COM port echo
Compatible with standard host terminal tools such as PuTTY/TeraTerm
Supports hot-plug
Class Driver
Location
{SDK}/component/usb/device/cdc_acm
API for Applications
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/cdc_acm/usbd_cdc_acm.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_cdc_acm_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handler, refer to Application Callback |
usbd_cdc_acm_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
usbd_cdc_acm_transmit |
Transmits data via bulk IN endpoint |
usbd_cdc_acm_notify_serial_state |
Transmits status via interrupt IN endpoint |
Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbd_cdc_acm_cb_t:
typedef struct {
u8(* init)(void);
u8(* deinit)(void);
u8(* setup)(usb_setup_req_t *req, u8 *buf);
u8(* received)(u8 *buf, u32 len);
void(* transmitted)(u8 status);
void (*status_changed)(u8 old_status, u8 status);
} usbd_cdc_acm_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called during class driver initialization for application resource setup |
deinit |
Called during class driver deinitialization for resource cleanup |
setup |
Called during control transfer SETUP/DATA phases to handle application-specific control requests |
received |
Called when bulk OUT transfer done, for application to handle the received data |
transmitted |
Called when bulk IN transfer done, for asynchronous bulk IN transfer status notification |
status_changed |
Called upon USB attach status changes for application to support hot-plug events |
Application Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbd_cdc_acm
The example defines an USB CDC ACM device, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for USB transparent communication device applcations.
HID Device Solution
Overview
The HID (Human Interface Device) class standardizes human input devices, using report descriptors to define data formats and control/interrupt transfers for host communication.
SDK provides:
HID keyboard and mouse device class drivers with following features:
For keyboard usage, endpoint configuration:
1 control IN/OUT endpoint for host control requests
1 interrupt IN endpoint for keypress reporting
1 interrupt OUT endpoint for host commands
For mouse usage, endpoint configuration:
1 control IN/OUT endpoint for host control requests
1 interrupt IN endpoint for movement/click reporting
Fully customizable descriptors
HID keyboard and mouse device application example with following features:
Basic keyboard and mouse input event simulation
Hot-plug support
Class Driver
Location
{SDK}/component/usb/device/hid
API for Applications
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/hid/usbd_hid.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_hid_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handler, refer to Application Callback |
usbd_hid_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
usbd_hid_send_data |
Transmit HID data with interrupt IN endpoint |
Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbd_hid_usr_cb_t:
typedef struct {
void(* init)(void);
void(* deinit)(void);
void(* setup)(void);
void(* transmitted)(u8 status);
void(* received)(u8 *buf, u32 len);
void (*status_changed)(u8 old_status, u8 status);
} usbd_hid_usr_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called during class driver initialization for application resource setup |
deinit |
Called during class driver deinitialization for resource cleanup |
setup |
Called during control transfer SETUP/DATA phases to handle application-specific control requests |
received |
Called when interrupt OUT transfer done, only for keyboard application to handle the received host command |
transmitted |
Called when interrupt IN transfer done, for asynchronous interrupt IN transfer status notification |
status_changed |
Called upon USB attach status changes for application to support hot-plug events |
Application Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbd_hid
The example defined a combined HID keyboard/mouse demo, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
HID keyboard example serves as a reference implementation for USB HID bidirectional communication devices, while the HID mouse example provides a reference implementation for USB HID unidirectional communication devices.
Mass Storage Device Solution
Overview
The MSC (Mass Storage Class) standard defines mass storage devices using SCSI command sets for read/write/erase operations on storage media.
SDK provides:
Standard MSC device class driver with following features:
Supports Bulk-Only Transport (BOT) protocol
Supports SD cards and RAM-based storage media
Configurable descriptors
Endpoint configuration:
1 control IN/OUT endpoint
1 bulk IN endpoint for data transmission
1 bulk OUT endpoint for data reception
MSC device application example with following features:
Supports USB hot-plug
Supports SD card hot-swap
Note
Use SD card hot-swap with caution, abrupt removal during transfers may cause filesystem corruption.
Class Driver
Location
{SDK}/component/usb/device/msc
API for Applications
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/msc/usbd_msc.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_msc_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handler, refer to Application Callback. |
usbd_msc_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
usbd_msc_disk_init |
Initializes storage media |
usbd_msc_disk_deinit |
Deinitializes storage media |
Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbd_msc_cb_t:
typedef struct {
void (*status_changed)(u8 old_status, u8 status);
} usbd_msc_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
status_changed |
Called upon USB attach status changes for application to support USB hot-plug events |
Application Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbd_msc
The example defines an USB MSC device, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for USB MSC device applcations.
FullMAC Device Solution
Overview
The INIC (Internet Network Interface Controller) enables a USB-based FullMAC implementation, functioning as a network interface card to provide host connectivity via USB.
For FullMAC details, refer to Supported ICs.
SDK provides:
INIC device class driver with following features:
Supports WiFi-only mode
Configurable descriptors
Endpoint configuration:
1 control IN/OUT endpoint
1 bulk IN endpoint for data transmission
2 bulk OUT endpoints for data reception
INIC device application example with following features:
Compatible with dedicated Linux FullMAC drivers (contact Realtek FAE)
Supports USB hot-plug
Class Driver
Location
{SDK}/component/usb/device/inic_dplus
API for Applications
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/inic_dplus/usbd_inic.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_inic_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handler, refer to Application Callback |
usbd_inic_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
usbd_inic_transmit_ctrl_data |
Transmits control IN data |
usbd_inic_transmit_data |
Transmits non-control IN data |
usbd_inic_receive_data |
Prepares to receive non-control OUT data |
Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbd_inic_cb_t:
typedef struct {
int(* init)(void);
int(* deinit)(void);
int(* setup)(usb_setup_req_t *req, u8 *buf);
int(* set_config)(void);
int(* clear_config)(void);
void(* transmitted)(usbd_inic_ep_t *in_ep, u8 status);
int(* received)(usbd_inic_ep_t *out_ep, u16 len);
void (*status_changed)(u8 old_status, u8 status);
void(*suspend)(void);
void(*resume)(void);
} usbd_uac_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called during class driver initialization for application resource setup |
deinit |
Called during class driver deinitialization for resource cleanup |
setup |
Called during control transfer SETUP/DATA phases to handle application-specific control requests |
set_config |
Notifies application layer when INIC driver becomes operational |
clear_config |
Notifies application layer when INIC driver becomes non-operational |
transmitted |
Called when non-control IN transfer done, for asynchronous non-control IN transfer status notification |
received |
Called when non-control OUT transfer done, for application to handle the received host command/data |
status_changed |
Called upon USB attach status changes for application to support hot-plug events |
suspend |
Called at suspend interrupt (GINTSTS.USBSusp) , used for application-specific suspend handling |
resume |
Called at resume interrupt (GINTSTS.WkUpInt) , used for application-specific resume handling |
Application Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbd_inic
The example defines an USB INIC device, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for USB FullMAC applcations.
Composite Device Solution
Overview
A USB composite device integrates multiple independent functions through a single physical USB interface. By combining distinct USB functional units as separate interfaces, the host system recognizes them as a collection of virtual devices, effectively addressing physical interface expansion limitations.
SDK provides composite device drivers and corresponding applcation examples with following function combinations:
CDC ACM + HID
CDC ACM + UAC
HID + UAC
Class Driver
Location
{SDK}/component/usb/device/composite
API for Applications
Composite Class Driver API
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/composite/usbd_composite_cdc_acm_hid.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_composite_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handlers:
|
usbd_composite_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
CDC ACM Class Driver API
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/composite/usbd_composite_cdc_acm.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_composite_cdc_acm_transmit |
Transmits CDC ACM data via bulk IN endpoint |
usbd_composite_cdc_acm_notify_serial_state |
Transmits CDC ACM status via interrupt IN endpoint |
HID Class Driver API
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/composite/usbd_composite_hid.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_composite_hid_send_data |
Transmits HID data via interrupt IN endpoint |
Composite Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbd_composite_cb_t:
typedef struct {
void (*status_changed)(u8 old_status, u8 status);
int (* set_config)(void);
} usbd_composite_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
set_config |
Notifies application layer that the class driver becomes operational |
status_changed |
Called upon USB attach status changes for application to support hot-plug events |
CDC ACM Application Callback
The class driver defines a CDC ACM application callback structure usbd_composite_cdc_acm_usr_cb_t:
typedef struct {
u8(* init)(void);
u8(* deinit)(void);
u8(* setup)(usb_setup_req_t *req, u8 *buf);
u8(* received)(u8 *buf, u32 len);
} usbd_composite_cdc_acm_usr_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called during class driver initialization for application resource setup |
deinit |
Called during class driver deinitialization for resource cleanup |
setup |
Called during control transfer SETUP/DATA phases to handle application-specific control requests |
received |
Called when bulk OUT transfer done, for application to handle the received bulk OUT data |
HID Application Callback
The class driver defines a HID application callback structure usbd_composite_hid_usr_cb_t:
typedef struct {
int(* init)(void);
void(* deinit)(void);
int(* setup)(usb_setup_req_t *req, u8 *buf);
void(* transmitted)(u8 status);
} usbd_composite_hid_usr_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called during class driver initialization for application resource setup |
deinit |
Called during class driver deinitialization for resource cleanup |
setup |
Called during control transfer SETUP/DATA phases to handle application-specific control requests |
transmitted |
Called when interrupt IN transfer done, for asynchronous interrupt IN transfer status notification |
Composite Class Driver API
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/composite/usbd_composite_cdc_acm_uac.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_composite_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handlers:
|
usbd_composite_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
CDC ACM Class Driver API
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/composite/usbd_composite_cdc_acm.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_composite_cdc_acm_transmit |
Transmits CDC ACM data via bulk IN endpoint |
usbd_composite_cdc_acm_notify_serial_state |
Transmits CDC ACM status via interrupt IN endpoint |
UAC Class Driver API
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/composite/usbd_composite_uac.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_composite_uac_config |
Configures audio parameters |
usbd_composite_uac_start_play |
Starts receiving audio data to ring buffer |
usbd_composite_uac_stop_play |
Stops audio data reception |
usbd_composite_uac_read |
Reads audio data from ring buffer for playing |
usbd_composite_uac_get_read_frame_cnt |
Gets queued audio frames count |
usbd_composite_uac_get_read_frame_time_in_us |
Gets queued audio frames time duration in us |
Composite Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbd_composite_cb_t:
typedef struct {
void (*status_changed)(u8 old_status, u8 status);
int (* set_config)(void);
} usbd_composite_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
set_config |
Notifies application layer that the class driver becomes operational |
status_changed |
Called upon USB attach status changes for application to support hot-plug events |
CDC ACM Application Callback
The class driver defines a CDC ACM application callback structure usbd_composite_cdc_acm_usr_cb_t:
typedef struct {
u8(* init)(void);
u8(* deinit)(void);
u8(* setup)(usb_setup_req_t *req, u8 *buf);
u8(* received)(u8 *buf, u32 len);
} usbd_composite_cdc_acm_usr_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called during class driver initialization for application resource setup |
deinit |
Called during class driver deinitialization for resource cleanup |
setup |
Called during control transfer SETUP/DATA phases to handle application-specific control requests |
received |
Called when bulk OUT transfer done, for application to handle the received bulk OUT data |
UAC Application Callback
The class driver defines an UAC application callback structure usbd_composite_uac_usr_cb_t:
typedef struct {
usbd_audio_cfg_t in;
usbd_audio_cfg_t out;
void *audio_ctx;
int(* init)(void);
int(* deinit)(void);
int(* setup)(usb_setup_req_t *req, u8 *buf);
int(* set_config)(void);
int(* status_changed)(u8 status);
int(* mute_changed)(u8 mute);
int(* volume_changed)(u8 volume);
int(* format_changed)(u32 freq, u8 ch_cnt, u8 byte_width);
int(* sof)(void);
} usbd_composite_uac_usr_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called during class driver initialization for application resource setup |
deinit |
Called during class driver deinitialization for resource cleanup |
setup |
Called during control transfer SETUP/DATA phases to handle application-specific control requests |
set_config |
Notifies application layer when UAC driver becomes operational |
status_changed |
Called upon USB attach status changes for application to support hot-plug events |
mute_changed |
Handles mute setting updates from USB host |
volume_changed |
Adjusts playback volume according to host-side volume changes |
format_changed |
Updates audio parameters (sample rate/channels) when modified by host |
sof |
Called upon SOF interrupt for clock synchronization |
Composite Class Driver API
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/composite/usbd_composite_hid_uac.h
API for Applications
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_composite_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handlers:
|
usbd_composite_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
HID Class Driver API
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/composite/usbd_composite_hid_bi_dir.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_composite_hid_send_data |
Transmits HID data via interrupt IN endpoint |
usbd_composite_hid_volume_ctrl |
Transmits volume control request to USB host via interrupt IN endpoint |
usbd_composite_hid_power_ctrl |
Transmits power control request to USB host via interrupt IN endpoint |
usbd_composite_hid_read |
Reads HID data from ring buffer |
usbd_composite_hid_get_read_buf_cnt |
Gets queued HID frames count |
usbd_composite_hid_ring_buf_is_full |
Check whether the HID received ring buffer is full |
UAC Class Driver API
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/composite/usbd_composite_uac.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_composite_uac_config |
Configures audio parameters |
usbd_composite_uac_start_play |
Starts receiving audio data to ring buffer |
usbd_composite_uac_stop_play |
Stops audio data reception |
usbd_composite_uac_read |
Reads audio data from ring buffer for playing |
usbd_composite_uac_get_read_frame_cnt |
Gets queued audio frames count |
usbd_composite_uac_get_read_frame_time_in_us |
Gets queued audio frames time duration in us |
Composite Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbd_composite_cb_t:
typedef struct {
void (*status_changed)(u8 old_status, u8 status);
int (* set_config)(void);
} usbd_composite_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
set_config |
Notifies application layer that the class driver becomes operational |
status_changed |
Called upon USB attach status changes for application to support hot-plug events |
HID Application Callback
The class driver defines a HID application callback structure usbd_composite_hid_usr_cb_t:
typedef struct {
int(* init)(void);
void(* deinit)(void);
int(* setup)(usb_setup_req_t *req, u8 *buf);
int(* set_config)(void);
int(* sof)(void);
void(* transmitted)(u8 status);
} usbd_composite_hid_usr_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called during class driver initialization for application resource setup |
deinit |
Called during class driver deinitialization for resource cleanup |
setup |
Called during control transfer SETUP/DATA phases to handle application-specific control requests |
set_config |
Notifies application layer that the class driver becomes operational |
sof |
Called upon SOF interrupt (GINTSTS.Sof) for timing-sensitive operations |
transmitted |
Called when interrupt IN transfer done, for asynchronous interrupt IN transfer status notification |
UAC Application Callback
The class driver defines an UAC application callback structure usbd_composite_uac_usr_cb_t:
typedef struct {
usbd_audio_cfg_t in;
usbd_audio_cfg_t out;
void *audio_ctx;
int(* init)(void);
int(* deinit)(void);
int(* setup)(usb_setup_req_t *req, u8 *buf);
int(* set_config)(void);
int(* status_changed)(u8 status);
int(* mute_changed)(u8 mute);
int(* volume_changed)(u8 volume);
int(* format_changed)(u32 freq, u8 ch_cnt, u8 byte_width);
int(* sof)(void);
} usbd_composite_uac_usr_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called during class driver initialization for application resource setup |
deinit |
Called during class driver deinitialization for resource cleanup |
setup |
Called during control transfer SETUP/DATA phases to handle application-specific control requests |
set_config |
Notifies application layer when UAC driver becomes operational |
status_changed |
Called upon USB attach status changes for application to support hot-plug events |
mute_changed |
Handles mute setting updates from USB host |
volume_changed |
Adjusts playback volume according to host-side volume changes |
format_changed |
Updates audio parameters (sample rate/channels) when modified by host |
sof |
Called upon SOF interrupt for clock synchronization |
Application Example
SDK provides following composite device applcation examples:
Path |
Description |
|---|---|
{SDK}/component/example/usb/usbd_composite_cdc_acm_hid/ |
CDC ACM virtual serial port and HID mouse composite device example |
{SDK}/component/example/usb/usbd_composite_cdc_acm_uac/ |
CDC ACM virtual serial port and UAC speaker composite device example |
{SDK}/component/example/usb/usbd_composite_uac_hid/ |
HID and UAC speaker composite device example |
Refer to the README.md in corresponding example directory for details.
These examples serve as reference implementations for USB composite device applcations.
Vendor-Specific Device Solution
Overview
The vendor-specific class and corresponding example provide reference design for USB vendor-specific device applications.
SDK provides:
Vendor-specific device class driver with following features:
Fully configurable device descriptor
Endpoint configuration:
1 control IN/OUT endpoint for enumeration
1 pair of bulk IN/OUT endpoints for bulk transfer test
1 pair of interrupt IN/OUT endpoints for interrupt transfer test
1 pair of isochronous IN/OUT endpoints for isochronous transfer test
Vendor-specific device application example with following features:
Co-work with vendor-specific host class defined in Vendor-Specific Host Solution
Supports bulk/interrupt/isochronous echo test
Supports hot-plug
Class Driver
Location
{SDK}/component/usb/device/vendor
API for Applications
API header file: {SDK}/component/usb/device/vendor/usbd_vendor.h
API |
Description |
|---|---|
usbd_vendor_init |
Initializes class driver with application callback handler, refer to Application Callback |
usbd_vendor_deinit |
Deinitializes class driver |
usbd_vendor_transmit_ctrl_data |
Transmits data via control IN endpoint |
usbd_vendor_transmit_bulk_data |
Transmits data via bulk IN endpoint |
usbd_vendor_receive_bulk_data |
Receives data via bulk OUT endpoint |
usbd_vendor_transmit_intr_data |
Transmits data via interrupt IN endpoint |
usbd_vendor_receive_intr_data |
Receives data via interrupt OUT endpoint |
usbd_vendor_transmit_isoc_data |
Transmits data via isochronous IN endpoint |
usbd_vendor_receive_isoc_data |
Receives data via isochronous OUT endpoint |
Application Callback
The class driver defines an application callback structure usbd_vendor_cb_t:
typedef struct {
int(* init)(void);
int(* deinit)(void);
int(* setup)(usb_setup_req_t *req, u8 *buf);
int(* set_config)(void);
int(* bulk_received)(u8 *buf, u32 len);
int(* intr_received)(u8 *buf, u32 len);
int(* isoc_received)(u8 *buf, u32 len);
void(* bulk_transmitted)(u8 status);
void(* intr_transmitted)(u8 status);
void(* isoc_transmitted)(u8 status);
void (*status_changed)(u8 old_status, u8 status);
} usbd_vendor_cb_t;
Where:
API |
Description |
|---|---|
init |
Called during class driver initialization for application resource setup |
deinit |
Called during class driver deinitialization for resource cleanup |
setup |
Called during control transfer SETUP/DATA phases to handle application-specific control requests |
set_config |
Used to notify application layer that the class driver becomes operational |
bulk_received |
Called when bulk OUT transfer done, for application to handle the received data |
intr_received |
Called when interrupt OUT transfer done, for application to handle the received data |
isoc_received |
Called when isochronous OUT transfer done, for application to handle the received data |
bulk_transmitted |
Called when bulk IN transfer done, for asynchronous bulk IN transfer status notification |
intr_transmitted |
Called when interrupt IN transfer done, for asynchronous interrupt IN transfer status notification |
isoc_transmitted |
Called when isochronous IN transfer done, for asynchronous isochronous IN transfer status notification |
status_changed |
Called upon USB attach status changes for application to support hot-plug events |
Application Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usbd_vendor
The example defines an USB vendor-specific device, refer to the README.md in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for USB vendor-specific device applcations.
Device Descriptor Customization
Overview
USB devices define their functionality through descriptors. The hierarchical structure of USB descriptors is illustrated below:
Where:
Each USB device contains exactly 1 Device Descriptor
One or multiple Configuration Descriptors (specified by bNumConfigurations), with only 1 active at any time
One or multiple Interface Descriptors per configuration (specified by bNumInterfaces), which can operate simultaneously
Zero, one or multiple Endpoint Descriptors per interface (specified by bNumEndPoints), which can operate simultaneously
Additional descriptor types include:
String Descriptors: Localized text descriptions for device/configuration/interface
Device Qualifier Descriptor: Required for dual-speed (HS/FS) devices
Other Speed Configuration Descriptor: Required for dual-speed (HS/FS) devices, alternate configuration for different speeds
Interface Association Descriptor (IAD): Mandatory for composite devices
Class-specific Descriptors: e.g., HID Report Descriptor
Note
Refer to USB specifications for complete descriptor definitions.
Data Structure
Standard host enumeration sequence:
Device Descriptor
Configuration Descriptor chain (active Configuration Descriptor and all subordinate descriptors)
String Descriptors (language ID, serial number, manufacturer, product)
Optional host requests:
Device Qualifier Descriptor (for dual-speed devices)
Other Speed Configuration chain (for dual-speed devices)
Class-specific descriptors (e.g., HID Report Descriptor for HID devices)
OS-specific descriptors (e.g., Microsoft OS String Descriptor @ index 0xEE)
Note
Unsupported descriptors should return STALL status without affecting functionality.
Based on standard USB host enumeration behavior, USB devices shall implement the following independent descriptor arrays:
Device Descriptor: Contains only the Device Descriptor
Configuration Descriptor:
One array per configuration
Includes the Configuration Descriptor plus all subordinate descriptors, e.g., Interface Descriptors and Endpoint Descriptors
String Descriptor
Language ID descriptor
Individual arrays for each string descriptor
Device Qualifier Descriptor: Contains only the Device Qualifier Descriptor
Other Speed Configuration Descriptor
One array per alternate speed configuration descriptor
Includes the Other Speed Configuration Descriptor plus all subordinate descriptors, e.g., Interface Descriptors and Endpoint Descriptors
May reuse Configuration Descriptor memory through dynamic descriptor type field replacement
Class-Specific Descriptor: Defined per device class specifications
Host-Specific Descriptor: Implemented per host requirements and application needs
Descriptor Customization
All the USB descriptors defined in USB device class drivers are open for modification, but for better compatibility, it is recommended to limit changes to:
VID/PID
Default: Realtek VID/PID
Custom VID: Requires USB-IF membership (https://www.usb.org/members)
Custom PID with Realtek VID: Contact Realtek FAE
Note
Using Realtek VID/PID doesn’t imply USB-IF compliance - certification still required.
String Descriptors
Customizable indices in:
Device Descriptor
iManufacturer
iProduct
iSerialNumber
Configuration Descriptor
iConfiguration
Interface Descriptor
iInterface
Note
USB device core driver provides ASCII-to-UNICODE conversion API (usbd_get_str_desc)
USB stack currently supports English strings only - other languages require custom language ID definitions
Endpoint Descriptor
Customizable parameters:
bEndpointAddress
wMaxPacketSize (recommend max specification-compliant value)
bInterval
Note
Default configurations guarantee SoC and USB specification compatibility. Any modifications require:
Thorough understanding of SoC limitations, refer to Hardware Features
Compliance with USB specifications
Device Connection Status Detection
For self-powered USB devices, when the USB connection status changes, the USB device class driver and application layer must promptly detect these events and implement corresponding handling procedures for hot-plug support and/or power consumption reduction.
The USB device core driver provides following APIs for connection status monitoring:
status_changed: Asynchronously detects USB connection status change events (refer to: USB Device Class Driver Callback)
usbd_get_status: Retrieves current device connection status (refer to: USB Device Core Driver API)
usbd_get_bus_status: Monitors USB bus DN/DP/suspend status (refer to: USB Device Core Driver API)
These APIs require USB register access after USB power on to return valid data, thus they should only be invoked after USB core driver initialization.
For pre-power status detection, external circuitry shall be employed - such as GPIO interrupt monitoring VBUS power events, refer to the reference design of USB insert detection circuit in Hardware Design Guide.
This hybrid hardware/software solution enables detection of the following USB connection status change events:
Event |
usbd_get_status |
status_changed |
VBUS GPIO Interrupt |
VBUS Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Reset (attached to USB host) |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_ATTACHED |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_INIT -> USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_ATTACHED |
N/A |
ON |
Reset (detached from USB host) |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_INIT |
N/A |
N/A |
OFF |
Reset (attached to USB charger) |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_INIT |
N/A |
N/A |
ON |
Attach to USB host |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_ATTACHED |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_DETACHED -> USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_ATTACHED |
Y (rising edge) |
OFF -> ON |
Detach from USB host |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_DETACHED |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_ATTACHED -> USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_DETACHED |
Y (falling edge) |
ON -> OFF |
Attach to USB charger |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_INIT or USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_DETACHED |
N/A |
Y (rising edge) |
OFF -> ON |
Detach from USB charger |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_INIT or USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_DETACHED |
N/A |
Y (falling edge) |
ON -> OFF |
Suspend |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_DETACHED |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_ATTACHED -> USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_DETACHED |
By USB host configuration |
By USB host configuration |
Resume |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_ATTACHED |
USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_DETACHED -> USBD_ATTACH_STATUS_ATTACHED |
By USB host configuration |
By USB host configuration |
Two typical application scenarios:
Software-Only Implementation (Recommended for Non-Power-Sensitive Applications)
When maintaining constant USB power is acceptable, the status_changed API provides sufficient software-based detection capability. Typical workflow includes:
Upon USB host disconnection: Terminate USB communications, deinitialize / re-initialize USB device, then await reconnection
Upon USB host connection: Resume USB communications
Hardware-Assisted Implementation (For Power-Critical Applications)
When minimizing power consumption during USB idle states is required, hardware solution such as GPIO-interrupt VBUS monitoring shall be implemented. Typical workflow includes:
Upon USB host disconnection or USB charger connection: Terminate USB communications, deinitialize USB device to enter low-power state
Upon USB host connection: Initialize USB device and resume communications
DRD Solution
Overview
DRD (Dual-Role Device) refers to USB devices capable of dynamically switching between host and device roles, providing enhanced flexibility for diverse application scenarios, e.g.:
Storage devices
Host mode: Connect to USB drives/printers
Device mode: Connect to PCs/mobile devices
Automotive devices, e.g., CarPlay devices
Industrial IoT devices: Flexible role switching between sensors (device) and controllers (host)
SDK provides a DRD reference implementation based on standard MSC host/device class drivers with following features:
Supports MSC device mode:
BOT (Bulk-Only Transport) protocol
SD card storage medium
Fully customizable descriptors
Supports MSC host mode:
FAT32-formatted MSC device support
Supports role switch from MSC device to MSC host
No SD card hot-swap support
No USB hot-plug support
Class Driver
MSC host, refer to Mass Storage Host Solution。
MSC device, refer to Mass Storage Device Solution。
Application Example
Location: {SDK}/component/example/usb/usb_drd
This example defines a dual-role mass storage device with runtime role switching capability, refer to the README.md file in the example directory for details.
This example serves as a reference implementation for USB DRD applcations.
USB Certification
USB certification generally refers to USB-IF certification, i.e. USB-IF compliance testing, which validates devices against USB-IF electrical, protocol and functional requirements to ensure interoperability, security and reliability. Certified devices are authorized to use USB logos.
While USB-IF certification is not mandatory, it is required when:
Products intend to use USB logos
Marketing materials claim USB specification compliance or certification
For certification procedures and requirements, refer to https://www.usb.org documentation or contact USB-IF authorized test labs.
Additional Compliance Requirements for USB Devices:
FCC/CE: Mandatory for USB devices sold in EU/US markets
ISO 26262: Required for automotive USB devices (functional safety)
Windows Logo Program: Necessary for “Certified for Windows” branding
MFi: Mandatory for Apple-specific USB accessories