TensorFlowLite-Micro (TFLM)
Supported SoCs
SoC |
RTL8721Dx |
RTL8720E |
RTL8713E |
RTL8726E |
RTL8730E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Supported Kernel |
KM4 |
KM4 |
KM4, DSP |
KM4, DSP |
CA32 |
Overview
TensorFlowLite-Micro (TFLM) is an open-source library, it is a port of TensorFlow Lite designed to run machine learning models on DSPs, microcontrollers and other devices with limited memory.
Ameba-tflite-micro is a version of the TFLM for Realtek Ameba SoCs with platform specific optimizations, and is available in ameba-rtos SDK.
More Information
Build TFLM
To build TFLM Library, enable tflite_micro configuration in SDK menuconfig.
Switch to GCC project directory in SDK
cd {SDK}/amebadplus_gcc_project
Run
menuconfig.pyto enter the configuration interface./menuconfig.py
Navigate through menu path to enable TFLM
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General--------- CONFIG TrustZone ---> ... CONFIG APPLICATION ---> GUI Config ---> ... AI Config ---> [*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
To build an example image such as
tflm_hello_world, run command:./build.py -a tflm_hello_world
More TFLM related examples are in the
{SDK}/component/example/tflite_microdirectory.
KM4
To build TFLM Library for KM4, enable tflite_micro configuration in SDK menuconfig.
Switch to GCC project directory in SDK
cd {SDK}/amebalite_gcc_project
Run
menuconfig.pyto enter the configuration interface./menuconfig.py
Navigate through menu path to enable TFLM
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General--------- CONFIG TrustZone ---> ... CONFIG APPLICATION ---> GUI Config ---> ... AI Config ---> [*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
To build an example image such as
tflm_hello_world, run command:./build.py -a tflm_hello_world
More TFLM related examples are in the
{SDK}/component/example/tflite_microdirectory.
DSP
To build TFLM Library for DSP, import {DSPSDK}/lib/tflite_micro as a project to the workspace in Xtensa Xplorer.
Click :menuselection:
File > Import > General > Existing Projects into Workspaceand choose the path of{DSPSDK}/lib/tflite_micro.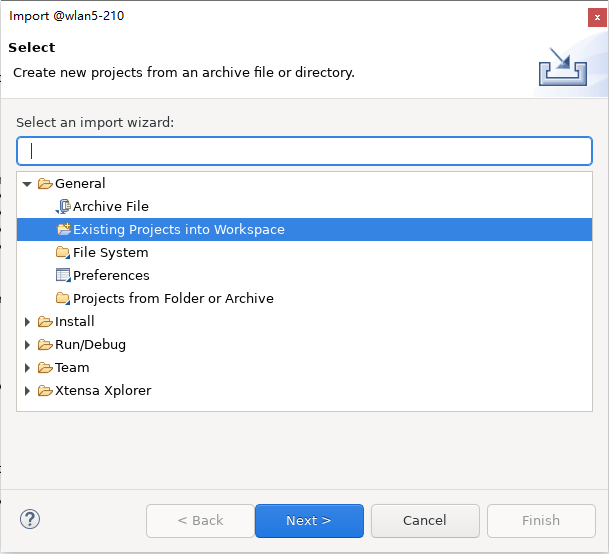
Set P to
libtflite_micro, C toHIFI5_PROD_1123_asic_UPGorHIFI5_PROD_1123_asic_wUPG, T toRelease, then clickBuild Active.The output library will be placed under
{DSPSDK}/lib/tflite_micro/project/bin/HIFI5_PROD_1123_asic_UPG/Release.
To build an example image, please refer to DSP Build for steps and the README in the example directory for software configurations.
TFLM related examples for DSP are in the
{DSPSDK}/example/tflite_microdirectory.
KM4
To build TFLM Library for KM4, enable tflite_micro configuration in SDK menuconfig.
Switch to GCC project directory in SDK
cd {SDK}/amebalite_gcc_project
Run
menuconfig.pyto enter the configuration interface./menuconfig.py
Navigate through menu path to enable TFLM
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General--------- CONFIG TrustZone ---> ... CONFIG APPLICATION ---> GUI Config ---> ... AI Config ---> [*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
To build an example image such as
tflm_hello_world, run command:./build.py -a tflm_hello_world
More TFLM related examples are in the
{SDK}/component/example/tflite_microdirectory.
DSP
To build TFLM Library for DSP, import {DSPSDK}/lib/tflite_micro as a project to the workspace in Xtensa Xplorer.
Click :menuselection:
File > Import > General > Existing Projects into Workspaceand choose the path of{DSPSDK}/lib/tflite_micro.
Set P to
libtflite_micro, C toHIFI5_PROD_1123_asic_UPGorHIFI5_PROD_1123_asic_wUPG, T toRelease, then clickBuild Active.The output library will be placed under
{DSPSDK}/lib/tflite_micro/project/bin/HIFI5_PROD_1123_asic_UPG/Release.
To build an example image, please refer to DSP Build for steps and the README in the example directory for software configurations.
TFLM related examples for DSP are in the
{DSPSDK}/example/tflite_microdirectory.
KM4
To build TFLM Library for KM4, enable tflite_micro configuration in SDK menuconfig.
Switch to GCC project directory in SDK
cd {SDK}/amebalite_gcc_project
Run
menuconfig.pyto enter the configuration interface./menuconfig.py
Navigate through menu path to enable TFLM
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General--------- CONFIG TrustZone ---> ... CONFIG APPLICATION ---> GUI Config ---> ... AI Config ---> [*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
To build an example image such as
tflm_hello_world, run command:./build.py -a tflm_hello_world
More TFLM related examples are in the
{SDK}/component/example/tflite_microdirectory.
To build TFLM Library, enable tflite_micro configuration in SDK menuconfig.
Switch to GCC project directory in SDK
cd {SDK}/amebasmart_gcc_project
Run
menuconfig.pyto enter the configuration interface./menuconfig.py
Navigate through menu path to enable TFLM
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General--------- CONFIG TrustZone ---> ... CONFIG APPLICATION ---> GUI Config ---> ... AI Config ---> [*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
To build an example image such as
tflm_hello_world, run command:./build.py -a tflm_hello_world
More TFLM related examples are in the
{SDK}/component/example/tflite_microdirectory.
Tutorial
MNIST Introduction
The MNIST database (Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology database) is a large collection of handwritten digits, widely used for training and validating machine learning models.
In this tutorial, MNIST database is used to show a full workflow from training a model to deploying it and run inference on Ameba SoCs with TFLM.
Example codes: {SDK}/component/example/tflite_micro/tflm_mnist.
Experimental Steps
Note
Step 1-4 are for preparing necessary files on a development machine (server or PC etc.). You can skip them and use prepared files in SDK to build the image.
Step 1: Train a Model
Use Keras (Tensorflow) or PyTorch to train a classification model for 10 digits of MNIST dataset.
The example uses a simple convolution based model, it will train several epochs and then test accuracy.
Run script
python keras_train_eval.py --output keras_mnist_conv
After training, Keras model is saved in SavedModel format in keras_mnist_conv folder.
Note
Due to the limited computation resources and memory of microcontrollers, it is recommended to pay attention to model size and operation numbers. In keras_train_eval.py, keras_flops library is used:
from keras_flops import get_flops
model.summary()
flops = get_flops(model, batch_size=1)
Run script
python torch_train_eval.py --output torch_mnist_conv
After training, PyTorch model is saved in .pt format, while a .onnx file is also exported for later conversion stage.
Note
Due to the limited computation resources and memory of microcontrollers, it is recommended to pay attention to model size and operation numbers. In torch_train_eval.py, ptflops library is used:
from ptflops import get_model_complexity_info
macs, params = get_model_complexity_info(model, (1,28,28), as_strings=False)
Step 2: Convert to Tflite
Apply post-training integer quantization on the trained model and output .tflite format.
Float model inference is also supported on Ameba SoCs, however, it is recommended to use integer quantization which can extremely reduce computation and memory with little performance degradation.
Refer to tflite official site for more details about integer-only quantization.
Run script
python convert.py --input-path keras_mnist_conv/saved_model --output-path keras_mnist_conv
Note
convert.py script details:
tf.lite.TFLiteConverter is used to convert SavedModel to .tflite format
Below settings for int8 quantization:
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model(saved_model_dir) converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT] converter.representative_dataset = repr_dataset converter.target_spec.supported_ops = [tf.lite.OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8] converter.inference_input_type = tf.int8 converter.inference_output_type = tf.int8 tflite_int8_model = converter.convert()
Run script
python convert.py --input-path torch_mnist_conv/model.onnx --output-path torch_mnist_conv
Note
convert.py script details:
onnx-tensorflow library is used to convert .onnx to SavedModel format
tf.lite.TFLiteConverter is used to convert SavedModel to .tflite format
Below settings for int8 quantization:
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model(saved_model_dir) converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT] converter.representative_dataset = repr_dataset converter.target_spec.supported_ops = [tf.lite.OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8] converter.inference_input_type = tf.int8 converter.inference_output_type = tf.int8 tflite_int8_model = converter.convert()
After conversion, the performance on test set will be validated using int8 .tflite model and two .npy files containing input array and label array of 100 test images are generated for later use on Ameba SoC.
Step 3: Optimize Tflite and Convert to C++
Use tflm_model_transforms tool from official tflite-micro repository:
git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/tflite-micro.git cd tflite-micro bazel build tensorflow/lite/micro/tools:tflm_model_transforms bazel-bin/tensorflow/lite/micro/tools/tflm_model_transforms --input_model_path=</path/to/my_model.tflite> # output will be located at: /path/to/my_model_tflm_optimized.tflite
Note
This tool can reduce .tflite size by running some TFLM specific transformations. It also re-align the tflite flatbuffer via the C++ flatbuffer API which can speed up inference on some Ameba SoCs.
This step is optional, but it is strongly recommended to run.
Run below commands to convert .tflite model and .npy test data to .cc and .h files for deployment:
python generate_cc_arrays.py models int8_tflm_optimized.tflite python generate_cc_arrays.py testdata input_int8.npy input_int8.npy label_int8.npy label_int8.npy
Step 4: Inference on SoC with TFLM
example_tflm_mnist.cc shows how to run inference with the trained model on test data, calculate accuracy, profile memory and latency.
Use netron to visualize the .tflite file and check the operations used by the model. Instantiate operations resolver to register and access the operations.
using MnistOpResolver = tflite::MicroMutableOpResolver<4>;
TfLiteStatus RegisterOps(MnistOpResolver& op_resolver) {
TF_LITE_ENSURE_STATUS(op_resolver.AddFullyConnected());
TF_LITE_ENSURE_STATUS(op_resolver.AddConv2D());
TF_LITE_ENSURE_STATUS(op_resolver.AddMaxPool2D());
TF_LITE_ENSURE_STATUS(op_resolver.AddReshape());
return kTfLiteOk;
}
Refer to tflite-micro official site for more details about running inference with TFLM.
Step 5: Build Example
Follow steps in Build TFLM to build the example image.